Media Formats
Your content is much more than just a file extension. Your media has some important properties:
- File container (mkv, mp4, avi, etc.)
- Video codec (H.264, HEVC, MPEG-2, etc.)
- Audio codec (DTS, AC-3, AAC, MP3, etc.)
- Subtitle format (SRT, VOBSUB, PGS, etc.)
And there can be individual properties within each of those. The combination of these things make up the “format” of your media and will determine how it can be played back. It will be used when decisions are made as to whether content should be Direct Played, Direct Streamed, or transcoded to your Plex app when playing content.
In order to get an idea about what sort of media you have, you’ll need to be able to examine this information.
Examining Your Media
The two common methods to examine the details of your media are either using the Plex Web App or using the “MediaInfo” application. In many cases, they’ll complement each other.
Using Plex Web App to Examine Media
If you have your Plex Media Server installed and have your content already scanned into your library, you can use the Plex Web App to access media information. This is particularly useful, because the information presented is exactly the information that the server has about the item.
Related Page: Plex Web App
Open the Media Info Window
First, browse to the details for the library item in which you’re interested. Then use the top action bar to access the Get Info action. (You can also access the action from the … context menu on posters in the library or discover pages.
Details
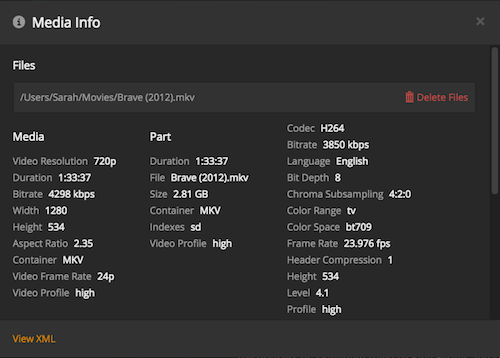
The Media Info window provides details about your media. At the top, the path and filename for your content is listed. Below that, you’ll see “Media” and “Part”, which provide some overall information. On the right side is “Video”, which contains details about the video stream within the file.
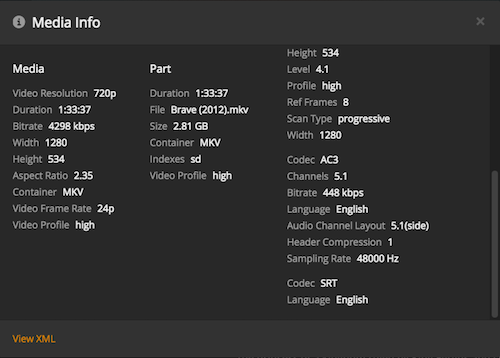
If you scroll within the window, you can access additional information. For instance, if the library item has multiple parts, they’ll be listed here and you can also see information such as details about “Audio” and “Subtitle” streams within the file.
The Media Info window is also available for other types of library content such as music files or photos.
XML Information / XML File
In some cases, you may also be asked to provide the “XML information” or the “XML file” for a library item. To get that, click the XML link at the bottom of the Media Info window:
You should be shown a webpage with the XML information.

If you’re asked to share the XML information, you can save that browser page and share the document.
Tip!: Depending on your browser, the XML may or may not show up directly. In some browsers, you can right-click and View Source if you see a blank window. For Safari, go to Preferences > Advanced and enable the “Show develop menu” option.
Using MediaInfo to Examine Media
If you’re trying to examine your media library prior to installing Plex Media Server, you can use an application such as “MediaInfo“. This could be useful if you’re trying to determine what sort of processor you’ll need for your computer or whether or not a NAS device will be sufficient for your needs. The MediaInfo application can provide a wealth of information about your content.
Note: While the MediaInfo app can provide useful information to you, it does not analyze media in the same way that Plex Media Server does, so there may be differences in the reported information. The information shown within Plex is the actual info used by the server, so it should be considered the “true” information, as far as Plex usage is concerned.
Related Page: MediaInfo Download
Once you load a media item in MediaInfo and switch to the “Tree” or “Text” view, you’ll see a lot of (possibly confusing) details about the item.
General Info
The “General” section contains basic information about the media item as a whole. Notable things here include the container format and overall bit rate.
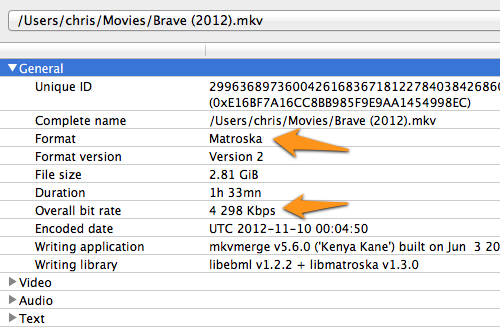
In this case, the item uses the Matroska (i.e. “MKV”) container and has an overall bitrate of ~4.3Mbps (~4300Kbps).
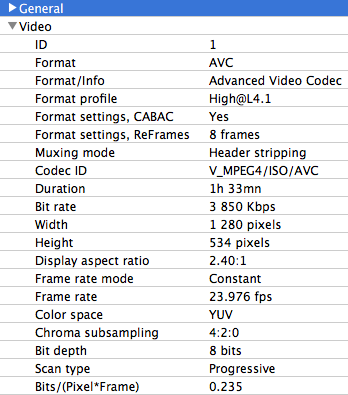
Video Info
Video information has details about the video stream within the file. There’s a lot of information in here that could be important, including: encoding type (H.264, HEVC, MPEG-2, etc.), encoding profile, resolution, bitrate, number of reference frames, and more.
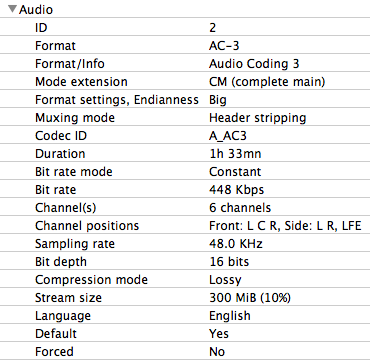
Audio Info
This is information about the audio stream(s) within the file. There may be more than one audio stream in some cases. Important details here include: audio format codec (AC-3, DTS, AAC, MP3, etc.), bitrate, and number of channels.
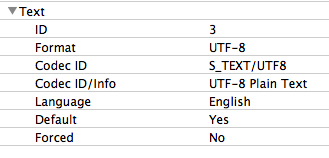
Subtitle Info
Some media may include one or more embedded subtitle streams. Important information here includes: the format and language.